Fault Tolerance
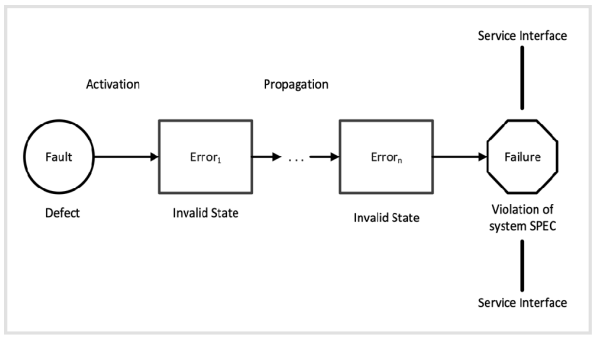
- Definition Fault:
Defect of a system that may cause an error.
- Definition Error:
Illegal system state.
- Definition Failure:
Occurs when an error reaches the service interface of a system, resulting in system behavior that is inconsistent with its specification.
Faults #
Internal vs External Fault #
- internal fault
- fault of a component
- external fault
- propagated failure of another component or from outiside the system
Fault categories #
- Physical
- Malfunction of hardware
- Design
- can be in hardware or software
- Interaction
- occurrs during operation, caused by the environment (operator error, radiation, …)
Failures #
Classifications of failures #
- Domain
- value / timing
- level of control
- signalled / unsignalled
- consequences
- minor / catastrophic
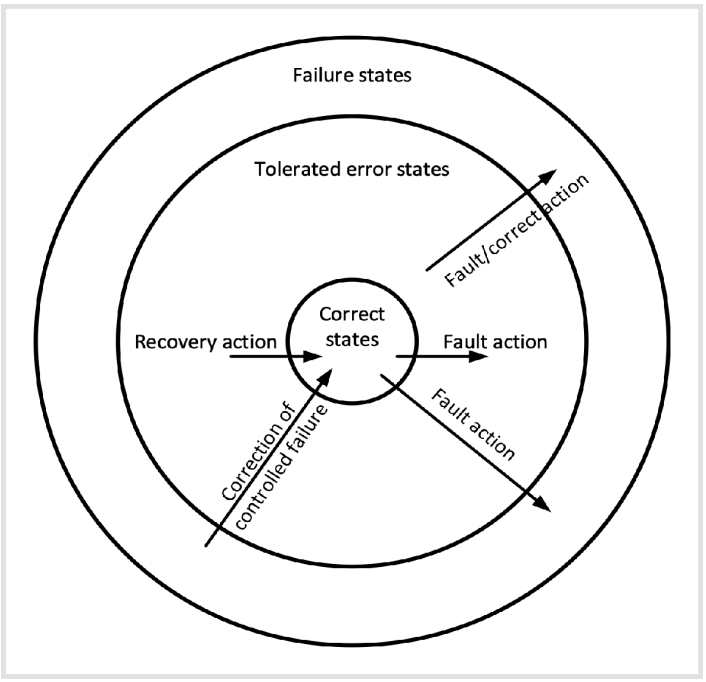
Tolerance #
Fault tolerant system #
- Never enters failure state
- Errors may occurr but never reach service boundary
- Some kind of redundancy needed
- Needs 3 steps
- Error detection
- Error analysis
- Recovery
Fail-controlled system #
- Allow recovery from failureusing special protocols
- e.g. it goes into a state from which corrective actions can be taken by an external controller
Fault prevention #
- Doing your best to prevent faults
- coding standards, firewalls, radiation shielding, …
Fault removal #
- Eliminate fault possibilities:
- Validation (check spec)
- Verification (prove system adheres to spec)
- Debugging -> find and eliminate faults