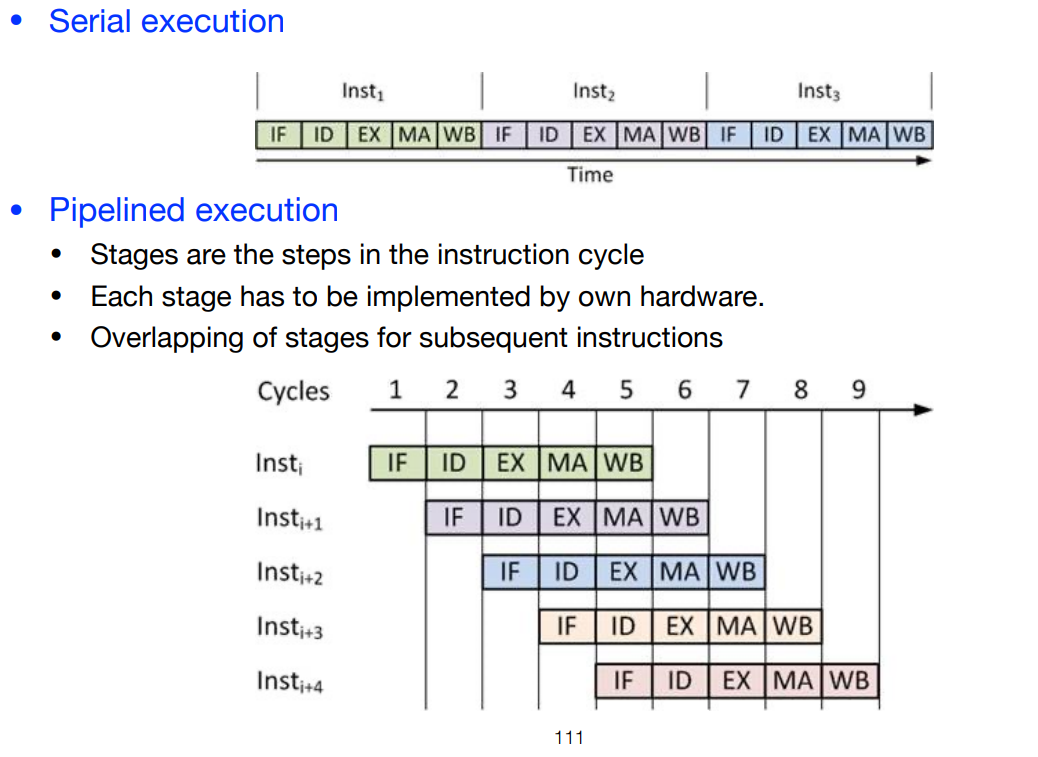
Instruction Pipelining
Instuction Cycle #
- IF
- Instruction Fetch
- Fetch instruction form memory (or i-cache) into instruction register
- Increment PC
- ID
- Instruction Decode
- Decode instruction
- Fetch register operands from register file
- EX
- Execution
- Perform ALU operation
- For load and store operations compute the address
- MA
- Memory Access
- Read or write from/to memory in case of load/store
- WB
- Write Back
- Write result back to register file
Pipelined execution #
- Processing split in steps
- steps are processed sequentially for a single object
- steps can be overlapped for different objects
- pipeline stage is the processing unit for a single step
- Pipeline consists of all its stages
- Advantage: higher thoughput
- Instructions can have higher latency: since they all have to go through all pipeline stages even if they don’t need to
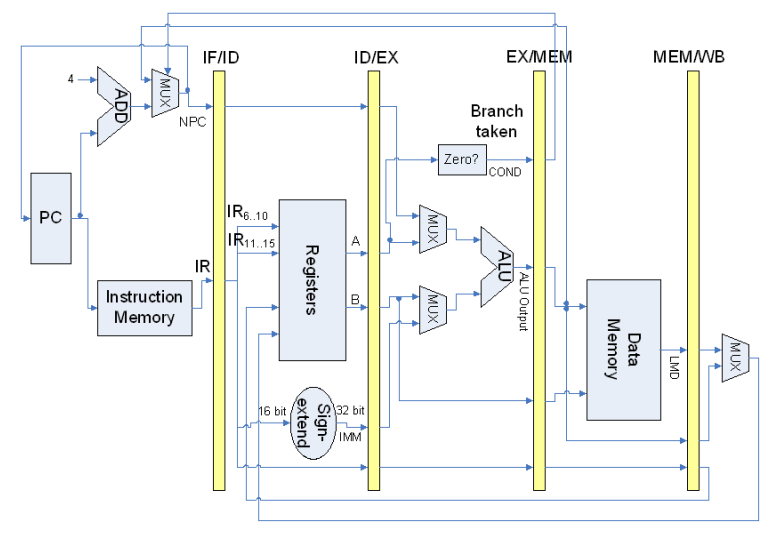
MIPS pipeline #
“Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipeline Stages”
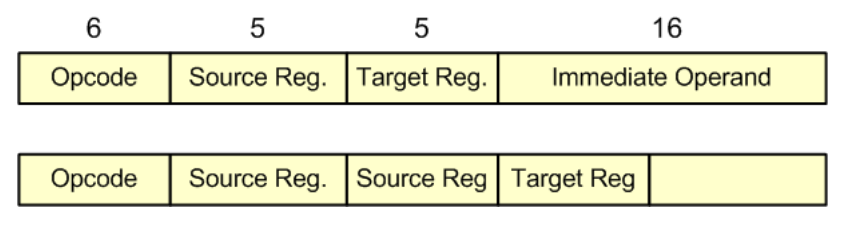
MIPS Instruction format #
Pipeline hazards #
- See Pipeline Hazards