Non-Volatile Memory
Memory that retains its storage.
Read Only Memory (ROM) #
- Contents inserted during production
Programmable ROM (PROM) #
- Write-once
- Programmable by burning fuses in the chip
Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) #
- Erasable, new information can be stored
- Read-only, information will stay until it is erased, it can’t be overwritten
- Charge stroed in the cells
- Whole memory is erased via ultraviolet light
Flash memory #
-
Also called “Electrically erasable PROM” (EEPROM)
-
Erase is done for an entire block
-
Works with strength of electric fields and required voltages to make something conduct.
-
The required voltage to make something conduct will give information about the state of transistors storing information
-
High negative voltage removes the charge
-
Isolation is damaged by reset, so number of writes is limited
- for NAND flash 10.000 - 1.000.000 writes for each cell -> distribution of writes to the same address over multiple cells
-
Used in Solid State Disc (SSD)
NAND Flash #
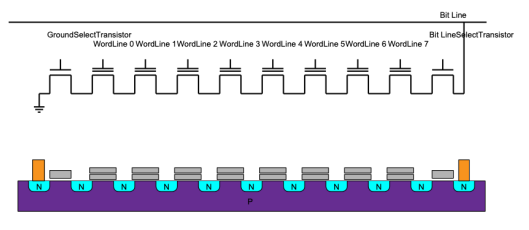
- For read:
- all word lines are set to a voltage so that the chate does not matter
- only for requested word the threshold voltage is applied
- if not charged the bit line gets low
- more compact / less wires than NOR Flash
NOR Flash #
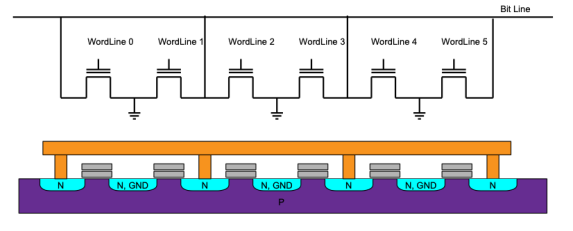
- Each cell can be read and written individually
Single- / Multi Level Cells (SLC/MLC) #
If the presence or absense of current is used to distinguish only two states, the cell stores 1 bit of information and is a SLC.
If distinguishing multiple levels of current, multiple bits can be stored in one cell (MLC).
Terminology in the web:
- SLC: 1 bit
- MLC: 2 bit
- TLC: 3 bit
- QLC: 4 bit
Fault tolerance #
-
Error correction code (ECC)
- Detection via additional parity bit
- Hamming code (71 bits instead of 64) can correct single bit errors
-
Chipkill memory (from IBM)
- Redundant Array of Independent Memory
- It can correct any single memory chip failure