Pipeline Hazards
-
Situations that prevent the next instruction to be processed in the next pipeline stage
-
Pipeline has to wait (stall), until the blocking instruction is finished
-
Classes:
- Resource hazards
- Data hazards
- Control hazards
Resource (Structural) hazards #
- Result from two instructions that are processed in different stages which require the same resource
- Example:
- Parallel writes to the register file:
- Arithemtic operation can write directly to register in the execute phase
- A load operation in the memory access phase
- Parallel access to memory in IF and MA
- Parallel writes to the register file:
Data Hazards #
-
Instruction accesses the same data as earier instructions should write but these are not yet finished
-
Data hazards result from Data Dependencies
-
Example:
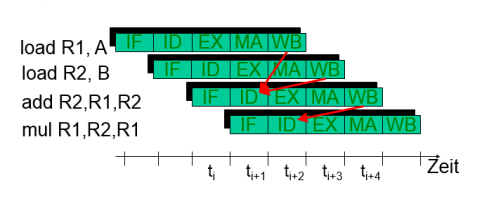
-
Problem: Instuction decode already fetches the operands
-
Data hazards can occur if data dependent instructions are executed only with a short delay in the pipeline
Classification #
- Read-after-Write (RAW)
- Implied by a true dependence
- Actually possible and has to be taken care of
- Write-after-Read (WAR)
- Implied by an anti dependence
- Can only happen if instruction j would write its target register before an ealrier instrucion i had the chance to read it (practically not possible)
- Write-after-Write (WAW)
- Implied by an output dependence
- Can only happen in pipelines where multiple stages can write (practically not possible)
Software solutions (by the compiler) #
- Insertion of
nopinstrucions to explicitly wait for a few cycles so that a hazard cannot occur - Even better: Reorder instructions to do other independent instructins first to wait for the data dependency to be resolved such that no hazard can occur
Hardware solutions #
-
Interlocking / Stalling
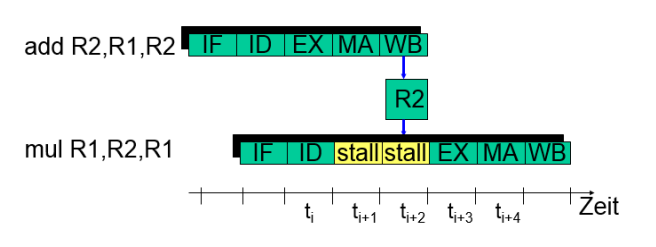
-
Forwarding: prematurely communicate insruction result directly to the waiting instruction. Don’t wait for th Write Back step.
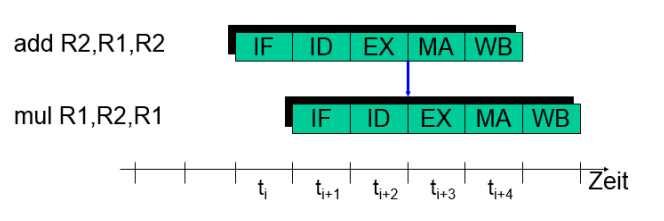
-
Both approaches can also be combined. (Not all dependences can be handled with forwarding, a load operation can not produce the result prematurely)
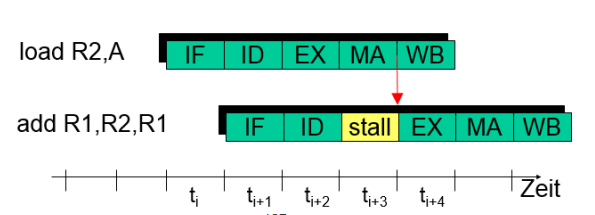
Control (Branch) hazards #
-
Next instruction cannot be fetched due to an yet undecided jump
-
Solutions:
-
Maybe try to compute condition and target in ID stage?
- Structural Hazard: ALU not available in ID stage -> More ALUs would be needed
- Data Dependence with previous arithemtic instruction -> RAW Hazard
- ID phase takes longer -> lower clockrate
-