Virtual Memory
-
OS is tasked to:
- select memory for code and data and load the program
- Manage and optimize usage of physical memory
- Processes may not use all the memory
- Processes may need more memory than available
- Unused data can be moved to storage
- Protection of data and code
-> Virtual memory enables / simpifies those tasks
-
Hardware support using Memory Management Unit (MMU)
-
Physical address space:
- Up to 64 bit, Intel E7: 46 bits used
-
Virtual address space:
- Intel E7: 48 bits used
- Linear address space for all processes
- Only OS can access physical addresses directly
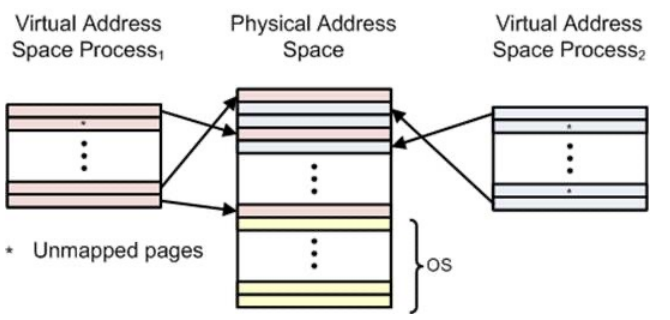
Pages and Frames #
- Virtual address space is organized in pages (typically 4kB but also larger ones exist 4MB)
- Physical address spaces is organized in frames, typically same size
- OS determines mapping from pages -> frames
- Mapping is applied for every access of virtual memory
- Mapping only consits of start of a virtual page, the offset in the page is same as offset on the frame
Address mapping via Page table #

-
Per process
-
Controlled by the OS
-
Sets access permissions in the mapping
-
Can store pages on storage if low on memory -> On page fault reload them
-
Impossible: 64 bit address space requires
pages (since a page =
bits large) and thus the table would have the size of 16 PBytes
Hierarchical page table #
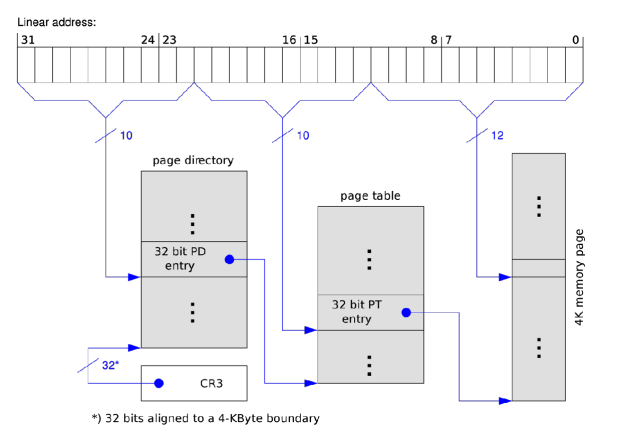
- Virtual address is split in 3 parts:
- To select a page table from the “page directory”
- To select a page in a page table
- To select the address in the page
Inverted page table #
- Store for each physical frame which virtual page is there
- Requires linear search
-> Alternatively hash-based schemes
Hash_Map<Virtual_Address, Physical_Address>- Hash with linked list on collision
- Both destroy cache locality: Information of subsequent pages is not near with respect to addresses in the inverted page table
-> Page table is also stored in memory
Page size tradeoff #
-
Larger Pages
- Smaller page tables
- Transfer is more efficient
- TLB will be used more efficietly
-
Smaller pages
- Less internal fragmentation
- Unused spaces of large pages also requires bandwidth to disk
- Starting small processes takes more time in larger pages