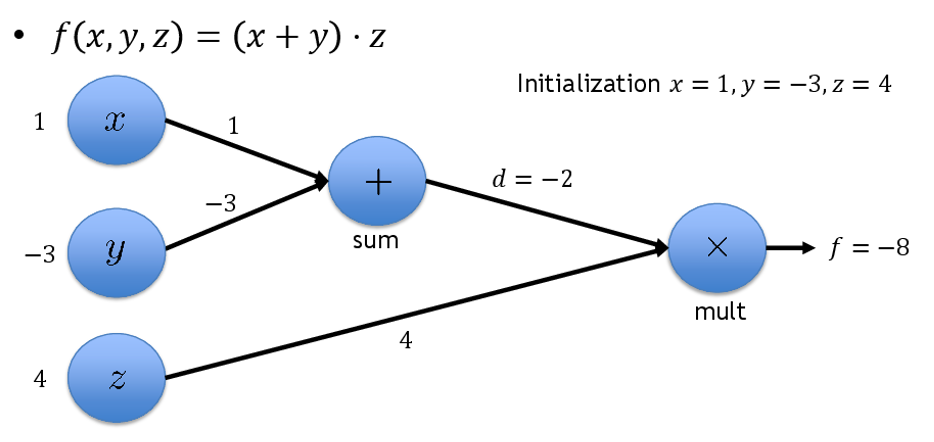
Computational Graph
-
The way computation can be modelled in a Neural Network .
-
Directional graph
-
Matrix operations are represented as compute nodes
-
Variables or scalar operators are vertex nodes
-
Directional edges show the flow of inputs to vertices
-
In a way the computational graph is equivalent to a syntax tree of a math expression
Evaluation #
Evaluating the neural network based on the Compute Graph and all the weights and input vector.
- Evaluate by tree walking
- starting at the leafs
Evaluation of the gradient #
For Gradient Descent we need to compute the gradient of the Loss Function (which is also part of the compute graph). So we are interested in:

- To do this, first evaluate the loss function as described above and let each node remember it’s intermediate result.
- Compute the partial derivatives for compute nodes.
Here:
;
;
;
;
- Walk the graph backwards
- We know the parial derivative of the last node
- We also know the evaluated values of the nodes contributing to the final node
- So each node we can annotate with the value of their derivative under the current evaluation
- Recursively do this until all leafs are reached
- According to the chain rule, the resulting derivative value must be multiplied with the parents derivative value