Neural Network
Basically a cascading of multiple Logistic Regressions . It is non linear score function. Also see: From Linear Regression to a Neural Network .
Use for Image Classification #
The score function would assign each label a certain probability, and the classifier would assign the label with the highest probability.
Structure of a neural network #
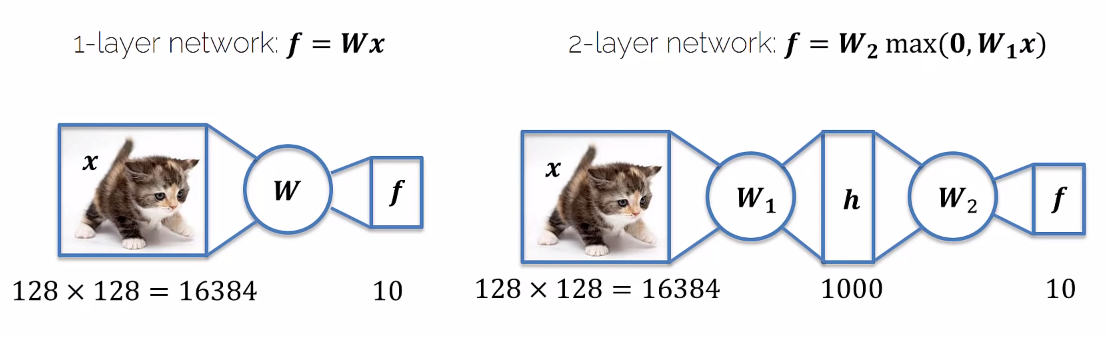
- One layer neual network is just a Linear Regression
- Each step of the evaluation of the neural network has its own dimensionality:
- Image: Pixels * Color channels
- Output: Number of Labels
- Hidden layers: Can be any number
Layer structure #
- Each layer consists of neurons
- Usually: every neuron is connected with every other neuron of the adjacent layers.
- The output of a neuron is sent to all its successors in the next layers. (Every successor will recieve the same value from it)
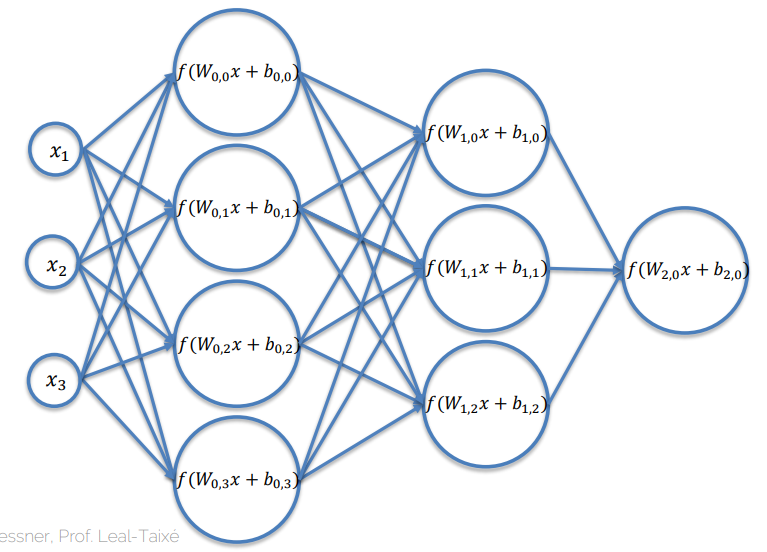
is the non-linear function: Activation Function
is the weight matrix (not an enty in on matrix)
- So
is a
matrix
- and
is a
matrix
- and
is a
matrix
- So
are scalars – one for each neuron
refers to the result of the previous layer
Comparison with neurons in a real brain #
- Neurons in a brain also get input from other neurons and as a response sends ouput to connected neurons.
- However the innermost conditions of the neuron are to this day not well known, so our simple mathematical model is at best inspired by the real neurons.
Training the neural network #
- Find
which contains all
and
to minimize the loss function
- Do this by for example with Backpropagation to do a Gradient Descent over the Loss Function
- There are many optimization methods, however
- Since the core of each neuron is a dot product, there are are usually multiple weights that would produce the same result. Use Regularization to find weights that help preventing Overfitting .
Debugging neural networks #
- Try to Overfit the network first. If the network can’t overfit on small amount of data, it might not be complex enough
- Visualize