Ambient Occlusion
The measure of how much a surface point is occluded by the environment. Analytically:
Where:
the ambient coefficient; how much ambient light is received
the normal oriented hemisphere
Visibility Function for direction
, outputs 0 or 1
angle between normal vector and
Original paper #
@inproceedings{miller1994efficient,
title={Efficient algorithms for local and global accessibility shading},
author={Miller, Gavin},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques},
pages={319--326},
year={1994}
}
https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/192161.192244
Note about why  is used for normalization:
#
is used for normalization:
#
Accounting for Area Foreshortening
, the resulting irradiance
at a
completely unoccluded surface point equals to :
Possible implementations #
- Prebaked an AO map by Raytracing (PBAO)
- Object Space Ambient Occlusion (OSAO)
- Screen Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO)
- Horizon Basesd Ambient Occlusion (HBAO)
- Alchemy Ambient Obscurance (AOO)
- Ground Truth based Ambient Occlusion (GTAO)
AO Pipeline #
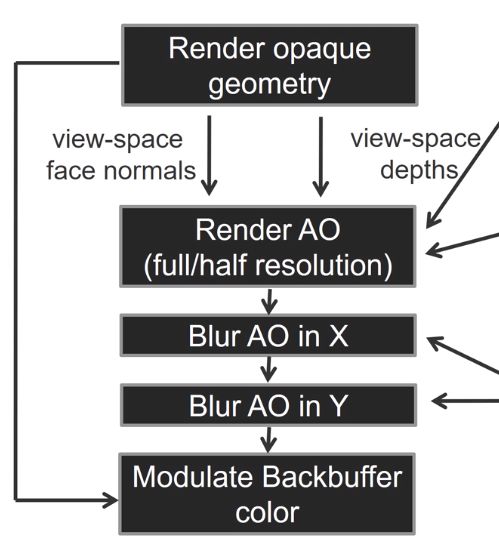
Bluring in X and Y separate will take two render passes but is in
. It a better complexity than a normal gaussian blur which
is
.
Problems #
AO leaving image problem #
Depth image based AO methods like SSAO or HBAO suffer AO that is leaving the view:
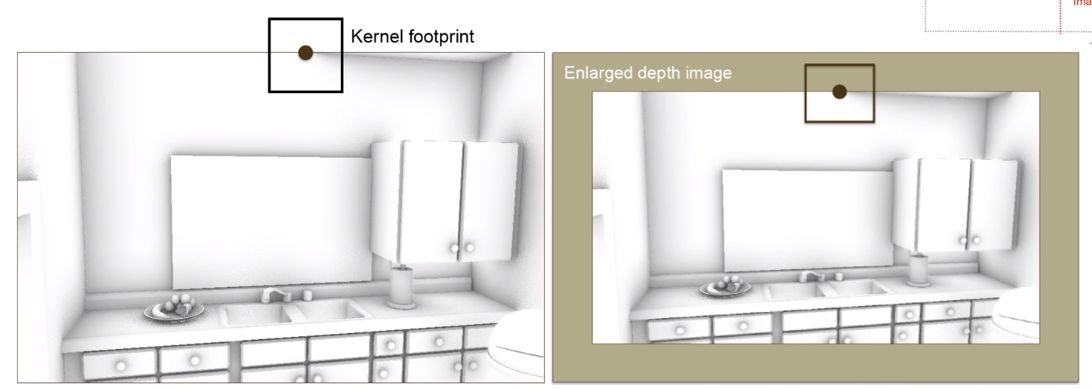
Solution: Render a bigger depth image
Discontinuity problem #
The computed AO from SSAO or HBAO both work with a radius. So the AO is not continuous.
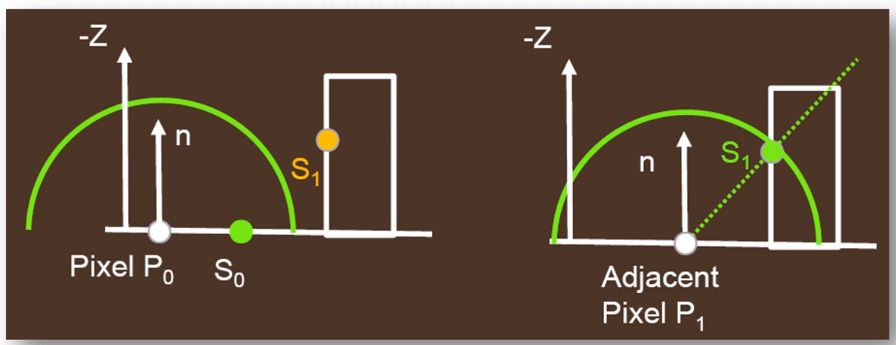
Noise #

Banding happens when samples are not chosen randomly but same random directions are used throughout the rendering.
To help with the noise, you can blur it.