BSP-Tree
“Binary Space Partitioning”
Paper #
@inproceedings{fuchs1980visible,
title={On visible surface generation by a priori tree structures},
author={Fuchs, Henry and Kedem, Zvi M and Naylor, Bruce F},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 7th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques},
pages={124--133},
year={1980}
}
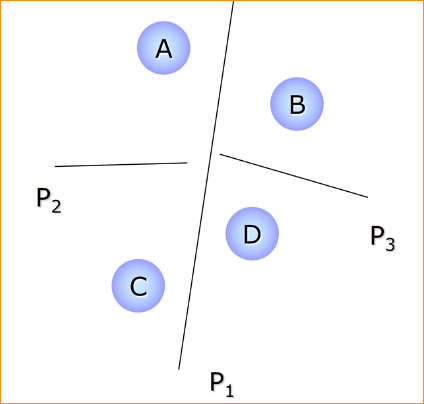
Characteristics #
- split planes don’t have to be axis aligned
- planes always split the remaining space in half
Ray test #
- Check if the ray intersects with the split plane
- if it does, recurse into both halfs
- if not recurse only into the children of the half the ray coinsides with
Calculating Visibility Order #
The Visibility Order can be calculated using a simple algorithm:
- DFS tree traversal
- always go to the child, which is on the same side from the splitting plane at that level as the viewer, first
Comparison to Octrees #
Pro:
- bsp-tree usually needs less nodes to divide all objects than an Octree
Con:
- it is not easy to find a good partioning